


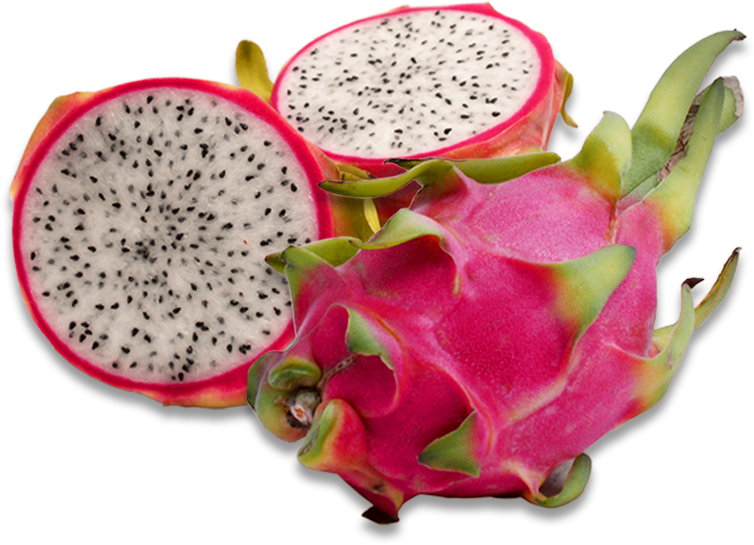
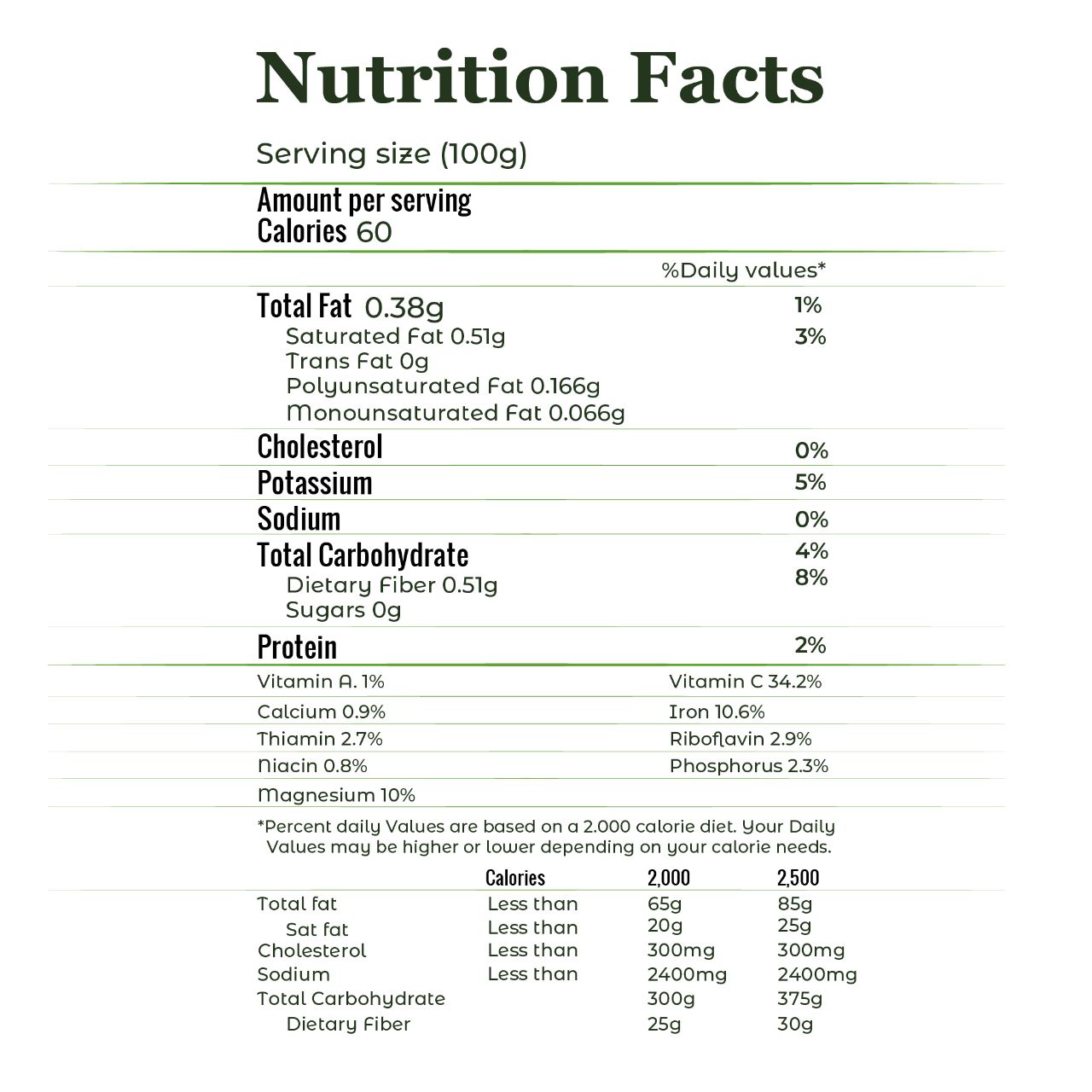
The pitaya and the pitahaya contain nutritional properties in content of vitamins C, B (B1 or thiamin, B3 or niacin and B2 or riboflavin), potassium, iron, calcium and phosphorus, in addition to being low in calories and helping digestion because they are rich in fiber.
the blood sugar level.
collagen production.
kidney stones.
cell aging.
and low in carbohydrates, its consumption is excellent for people who do slimming diets.

for the formation of bones and teeth.
the absorption of iron (essential to avoid or combat anemia).
the immune system by stimulating the production of white and red blood cells and platelets.
regulate intestinal transit by making their seeds have a laxative effect.
The pitaya and the pitahaya contain nutritional properties in content of vitamins C, B (B1 or thiamin, B3 or niacin and B2 or riboflavin), potassium, iron, calcium and phosphorus, in addition to being low in calories and helping digestion because they are rich in fiber.

kidney stones.
the blood sugar level.
collagen production.
cell aging.
for the formation of bones and teeth.
the immune system by stimulating the production of white and red blood cells and platelets.
regulate intestinal transit by making their seeds have a laxative effect.
the absorption of iron (essential to avoid or combat anemia).
and low in carbohydrates, its consumption is excellent for people who do slimming diets.
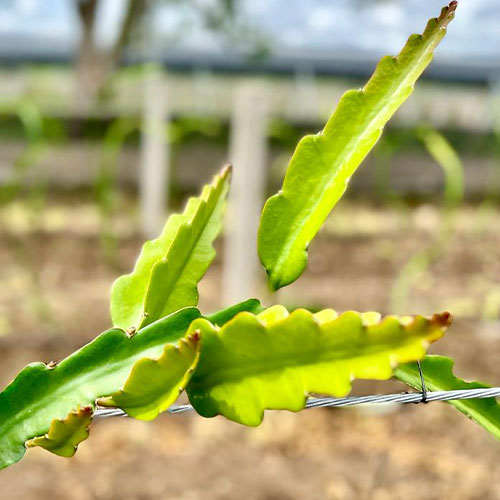
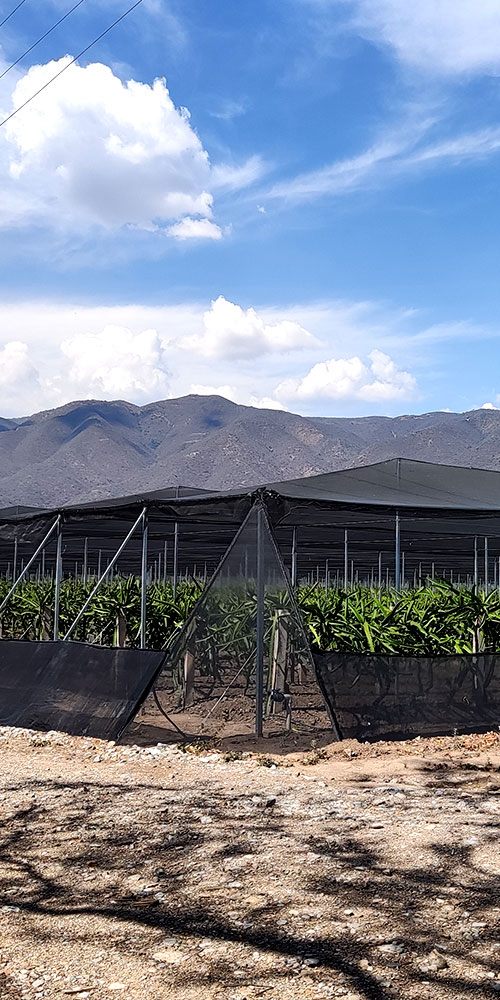
The pitahaya is a cactus plant, and as such, resistant to drought. The plant is a rustic, succulent cactus with long triangular stems. It tends to get entangled in nearby trees, feeding on the moisture from their barks and climbs up the branches eight or ten meters above the ground without penetrating the ground.
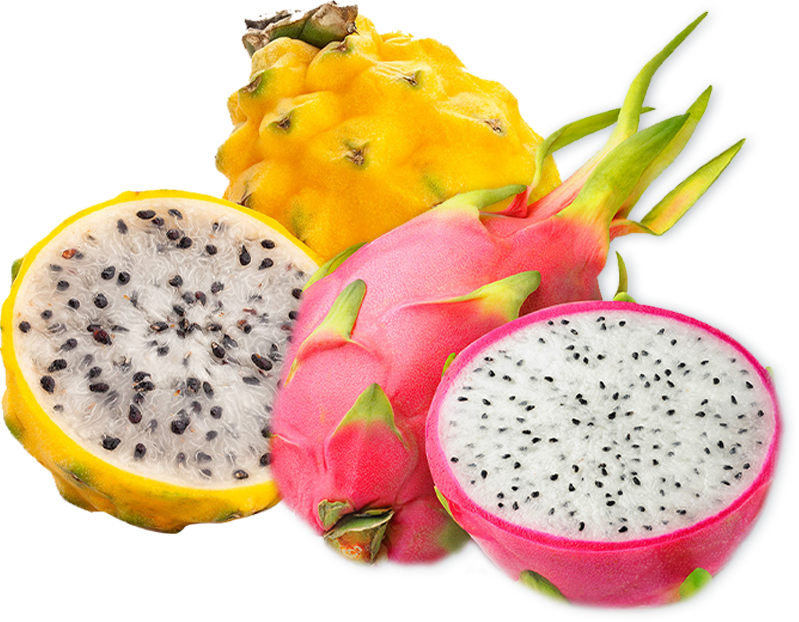
Its fruit is ovoid, rounded and elongated, with red, white or yellow pulp and small black seeds; its flavor is less sweet than that of the pitaya.
The pitahaya is an epiphytic, climbing plant and its development can be invasive on any surface that can be adapted. It is a perennial crop for at least 25 years, adaptable to semi-arid, semi-desert climates, tolerable to drought, saline soils, saline waters, with a great capacity for survival and resistance to pests and diseases.
Lacking architecture that supports its own weight, it has adapted to rigid surfaces for its development, usually trees that provide partial shade.

The propagation of the plants is done through cuttings, these, in turn, develop superficial roots that anchor the plant to the soil, through which they absorb water, minerals and nutrients. If the plant does not develop enough roots in the soil, it usually develops them in the aerial part, thus looking for a support of the same weight and moisture absorption.
The best time to sow cuttings is in the autumn equinox, since the days are shortened, therefore, the plants stop emitting flowers and concentrate on the elongation of their stems. Therefore, growth and development is much more successful than at other times of the year.
Although the crop is not demanding in water, it requires a particular dose and to determine this dose it is necessary to consider certain variables that determine it (type of soil, hydraulic conductivity of the soil, temperature, crop evapotranspiration).
Pruning is a task that directs the energy of the plant, be it to produce (fruit) or reproduce (vegetative growth).
The nutrition of the crop is defined in 3 major elements (N) nitrogen, it is in charge of cell elongation and apical growth of the plant, (P) phosphorus, it is in charge of promoting new and better roots and (K) potassium in charge of flowers and fruits.
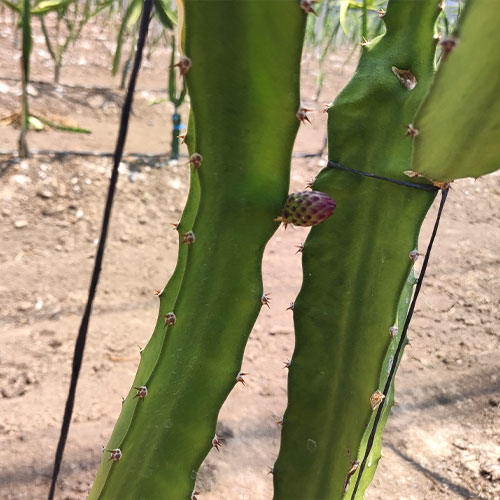
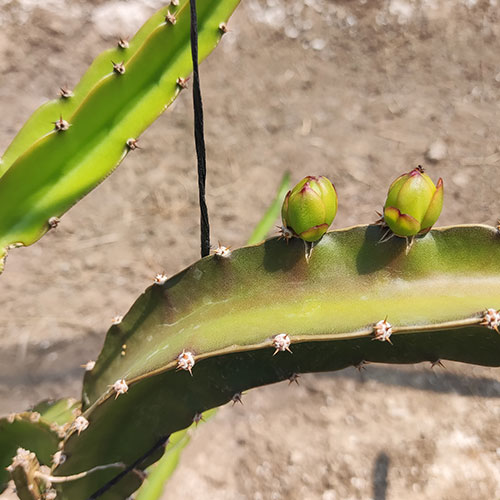
The harvest is carried out between 35 and 40 days after the opening of the flower, depending on the variety.
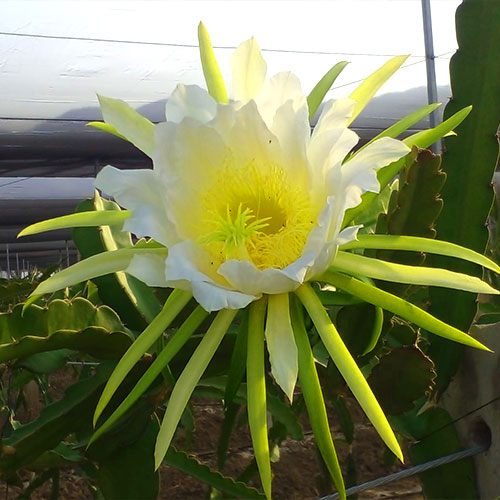
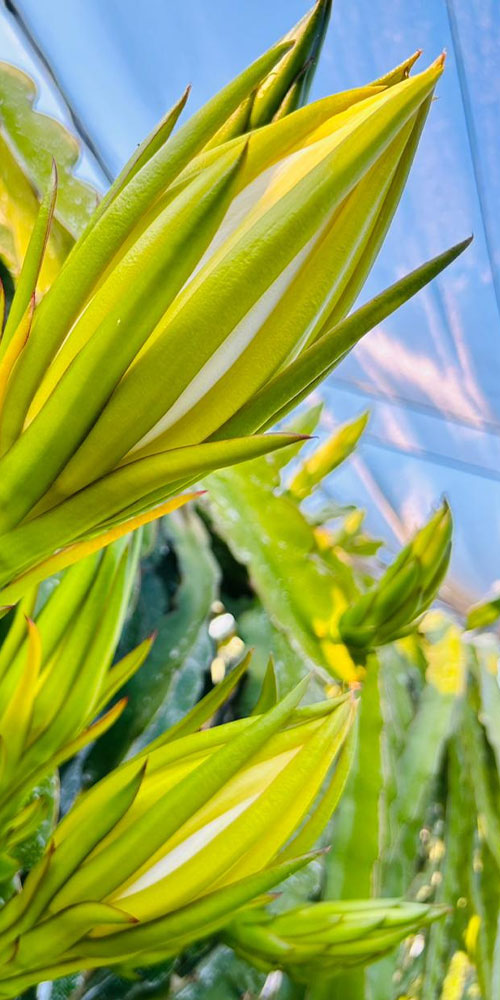
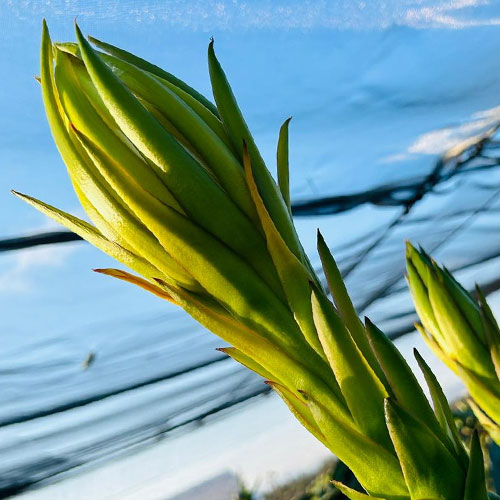
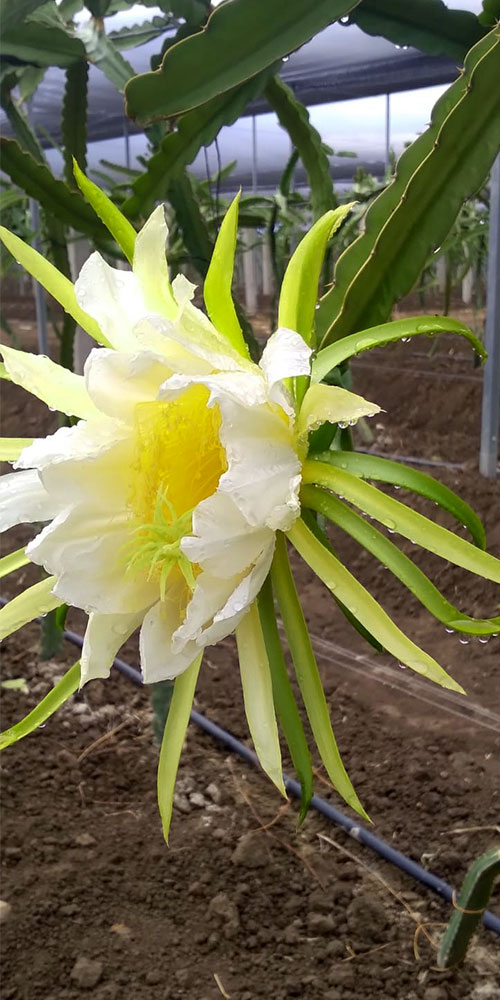
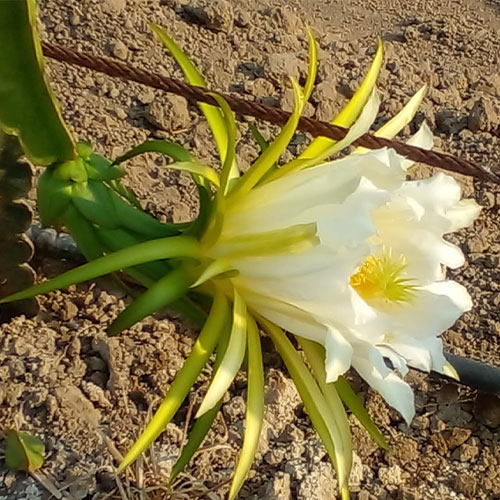
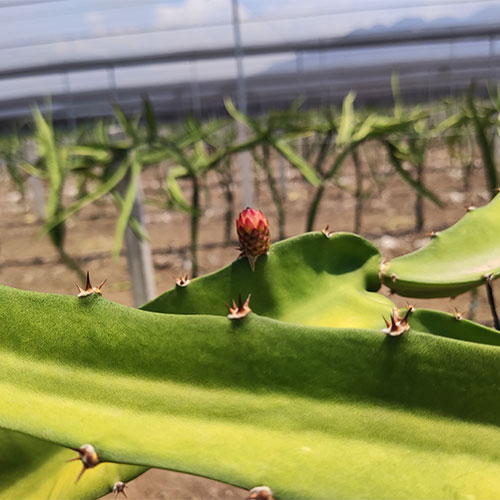











It is a night flower that opens facing the moonlight and only lasts one night, which is why it is also known as a one-night flower. The pitahaya flower, which is tubular, hermaphrodite like most cacti, is beautiful but brief, as it appears dazzling in the morning and as it begins to feel the heat of the sun it becomes dehydrated suddenly.
The pitahaya is known as dragon fruit because the plant that produces it climbs over the trunks of the trees and intertwines giving the shape of the body of a dragon, a mythological animal that is very popular in Asia, mainly in China.

There are more than 600 species.
Only two varieties are edible, the yellow pitahaya and the red pitahaya.
The Pitahaya flower is the largest of all cacti.
It contains a greater amount of vitamin C and antioxidants.
Hacienda de Buena Vista, 75914 Ajalpan, Pue.
sales@buenavistafarms.mx